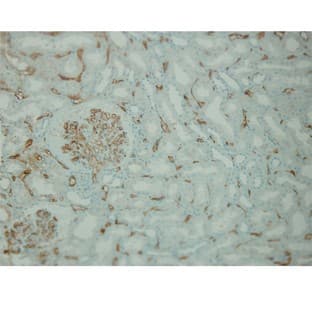
Supplier:
Boster ImmunoleaderCat no: PA1211
Polyclonal Anti-COX2
Prices direct from Boster Immunoleader
Quick response times
Exclusive Absave savings/discounts
SPECIFICATIONS
Price
200.00 USD
Catalog Number
PA1211
Size
100ug/vial
Applications
IHC, WB
Reactivities
Hum, Mouse, Rat
Form
Lyophilized
Format
Each vial contains 5mg BSA, 0.9mg NaCl, 0.2mg Na2HPO4, 0.05mg Thimerosal, 0.05mg NaN3.
Gene Id
PTGS2
References
1. Salmenkivi, K.; Haglund, C.; Ristimaki, A.; Arola, J.; Heikkila, P. : Increased expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in malignant pheochromocytomas. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 86: 5615-5619, 2001. \n2. Liu, C. H.; Chang, S.-H.; Narko, K.; Trifan, O. C.; Wu, M.-T.; Smith, E.; Haudenschild, C.; Lane, T. F.; Hla, T. : Overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 is sufficient to induce tumorigenesis in transgenic mice. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 18563-18569, 2001.\n3. Wilkinson-Berka, J. L.; Alousis, N. S.; Kelly, D. J.; Gilbert, R. E. : COX-2 inhibition and retinal angiogenesis in a mouse model of retinopathy of prematurity. Invest. Ophthal. Vis. Sci. 44: 974-979, 2003.\n4. Brewer, J. A.; Khor, B.; Vogt, S. K.; Muglia, L. M.; Fujiwara, H.; Haegele, K. E.; Sleckman, B. P.; Muglia, L. J. : T-cell glucocorticoid receptor is required to suppress COX-2-mediated lethal immune activation. Nature Med. 9: 1318-1322, 2003.
Swiss Prot
P35354
Storage Temp
\"At -20 degree C for one year. After reconstitution, at 4 degree C for one month. It can also be aliquotted and stored frozen at -20 degree C for a longer time.\nAvoid repeated freezing and thawing. \n\"\n
Additional Info
A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence at the N-terminal of human COX-2, different from the related rat sequence by two amino acids.
Scientific Background
Cyclooxygenase (Cox) is the key enzyme in conversion of arachidonic acid to PGs, and two isoforms, Cox-1 and Cox-2, have been identified. Cox-2 gene encodes an inducible prostaglandin synthase enzyme that is overexpressed in adenocarcinomas and other tumors. Deletion of the murine Cox-2 gene in Min mice reduced the incidence of intestinal tumors, suggesting that it is required for tumorigenesis. This gene is localized to sites associated with retinal blood vessels, and plays an important role in blood vessel formation in the retina. And the glucocorticoid receptor suppression of COX-2 is also crucial for curtailing lethal immune activation, and suggest new therapeutic approaches for regulation of T-cell-mediated inflammatory diseases.
More from Boster Immunoleader
Applications
WB
Reactivities
Hum
Applications
ELISA, WB
Reactivities
Hum
Applications
ELISA, IHC, WB
Reactivities
Hum
Applications
ELISA, WB
Reactivities
Mouse
Applications
ELISA, IHC, WB
Reactivities
Rat
Applications
BNI, ELISA, IHC, IP, WB
Reactivities
Mouse
Conjugates
Unconj, Agarose, AP, Biotin, Gold, HRP, BE, GE, YE, OE, RE, FRE, NIR, ONFC
Applications
BNI, ELISA, IHC, IP, WB
Reactivities
Rat
Latest promotions
Buy any polyclonal or monoclonal antibody from our extensive range of pre-made antibodies and for a limited time only receive a $50 discount!(T&C apply:...
New brilliant antibodies, and new lower prices!For flow cytometry reagents in general, \"bright is better.\" The violet-excitable BD Horizon™ BV421 and...
10% Discount on 2 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody Service. With over 20 years experience, SDIX has developed into the premier US custom antibody producer,...
For the past decade scientists have extensively used ATS secondary toxin conjugates to make their own targeted toxins for in vitro use.The ability to combine...
We're so sure that you'll prefer Cayman Assay kits over your present brand that we're willing to give you a free assay kit to prove it!
Did your supplier increase the price of Fetal Bovine Serum? Did they substitute the US Origin with USDA? Well say no more! Innovative Research is still...
Bulk Cytokines with Custom Vialing.20 - 50% off cytokines, growth factors, chemokines and more...For a limited time Cell Sciences is offering substantial...
Are you planning to have a customised antibody made for your research?Since 2000, Everest has been producing a catalog containing thousands of affinity...
Top suppliers
Agrisera AB
11 products
Biotrend
Biosensis
969 products
ABBIOTEC
3011 products
SDIX
1 products
Spring Bioscience
2291 products
Cell Signaling Technology
4976 products
Rockland Immunochemicals, Inc.
7592 products
Boster Immunoleader
1533 products
OriGene Technologies Inc.
5281 products
Maine Biotechnology Services
227 products
BD (Becton, Dickinson and Company)
1 products
ABNOVA CORPORATION
Randox Life Sciences
1502 products